🧬 Extracellular Vesicles: Key Drivers of Tumor Progression in Prostate Cancer:
Context:
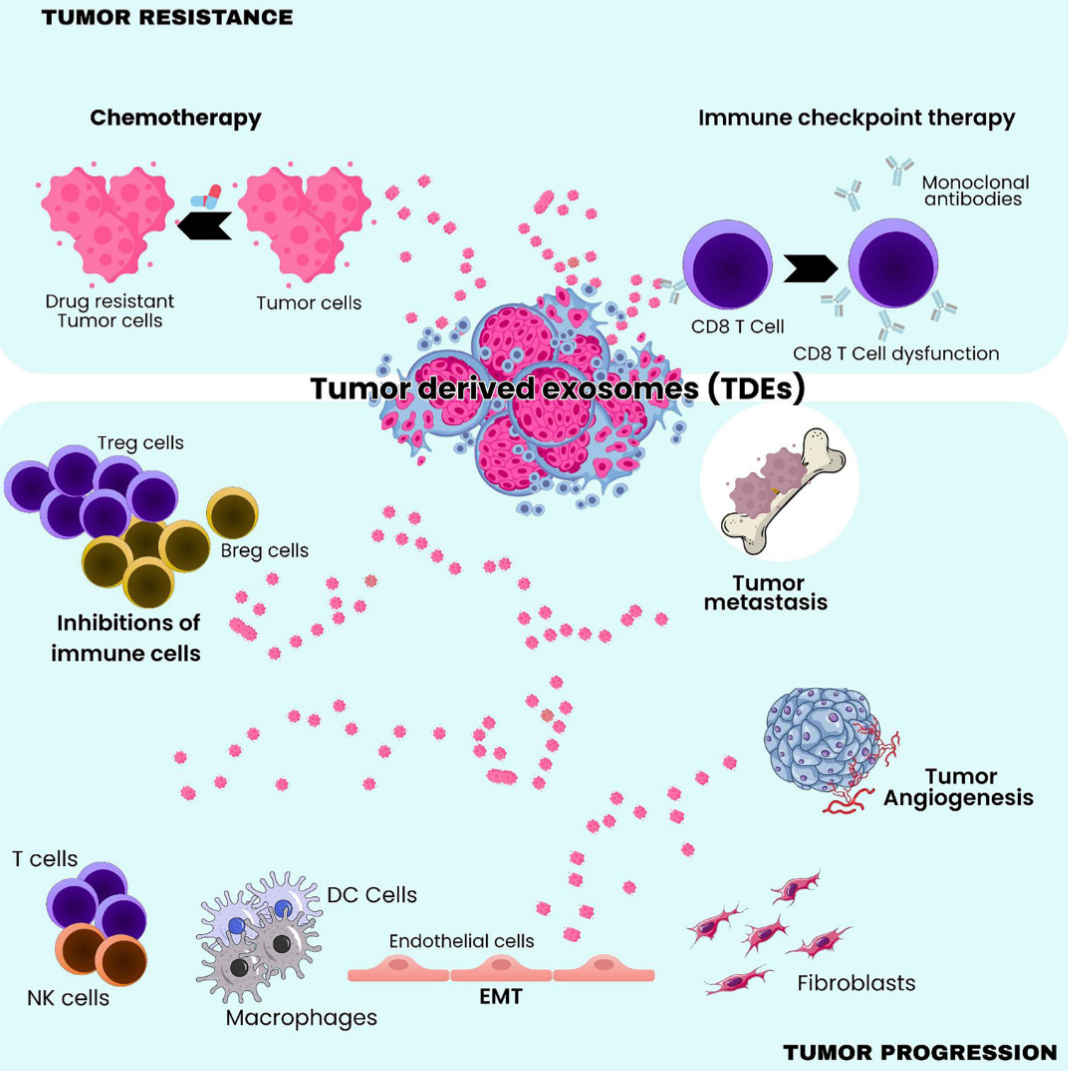
This review highlights how extracellular vesicles (EVs) particularly exosomes shape nearly every stage of prostate cancer (PCa) development and progression.
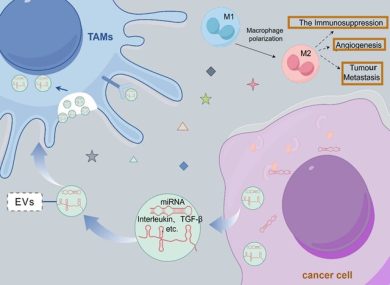
EVs released by tumor cells transport miRNAs, proteins, lipids, AR–associated molecules, and metabolic factors that regulate tumor growth, epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), metastasis, drug resistance, and immune modulation.
Of special interest is their role in androgen receptor (AR) signaling, a central pathway in PCa biology.
Insight:
What stands out is how EVs act as mobile extensions of prostate cancer cells.
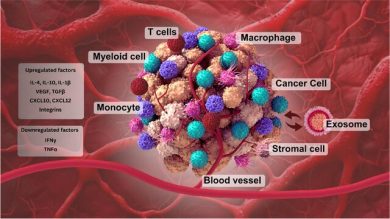
They don’t just reflect the tumor state they actively remodel the tumor microenvironment by:
-promoting AR-driven proliferation and survival,
-preparing pre-metastatic niches in bone and lymph nodes,
-transferring resistance to anti-androgen therapies such as enzalutamide,
-suppressing T-cell activity through immunomodulatory cargo,
-and reprogramming fibroblasts and macrophages into pro-tumor phenotypes.
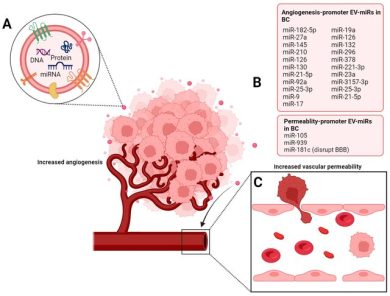
The precision of this communication especially through miR-21, miR-141, miR-375, and AR-V7–containing EVs underscores their importance as both biomarkers and functional mediators.
Scientific Significance:
EVs may transform prostate cancer management by enabling:
-liquid biopsy biomarkers for early detection and therapy monitoring,
-EV-based predictive signatures for therapy resistance (e.g., AR-V7 EVs for anti-androgen response),
-engineered EVs as delivery vehicles for siRNA, miRNA inhibitors, or targeted drugs,
-therapeutic blockade of EV release to reduce tumor progression and metastatic spread.
As research advances, EV-centered approaches may complement or even reshape existing androgen-targeted therapies.
Source:
📄 The emerging role of extracellular vesicles in prostate cancer theranostics: current insights and future prospects
DOI:10.1007/s12254-025-01083-y