🧬 Small Extracellular Vesicles: A Promising Frontier in Pancreatic Cancer Therapy
Context:
Pancreatic cancer remains one of the deadliest malignancies, with extremely low early-detection rates, dense stromal barriers, and limited patient response to standard chemotherapies like gemcitabine and FOLFIRINOX.
This comprehensive review highlights small extracellular vesicles (sEVs) as a rapidly advancing therapeutic platform capable of overcoming key challenges in pancreatic cancer (PC), including drug resistance, immune evasion, and poor drug penetration.
Insight:
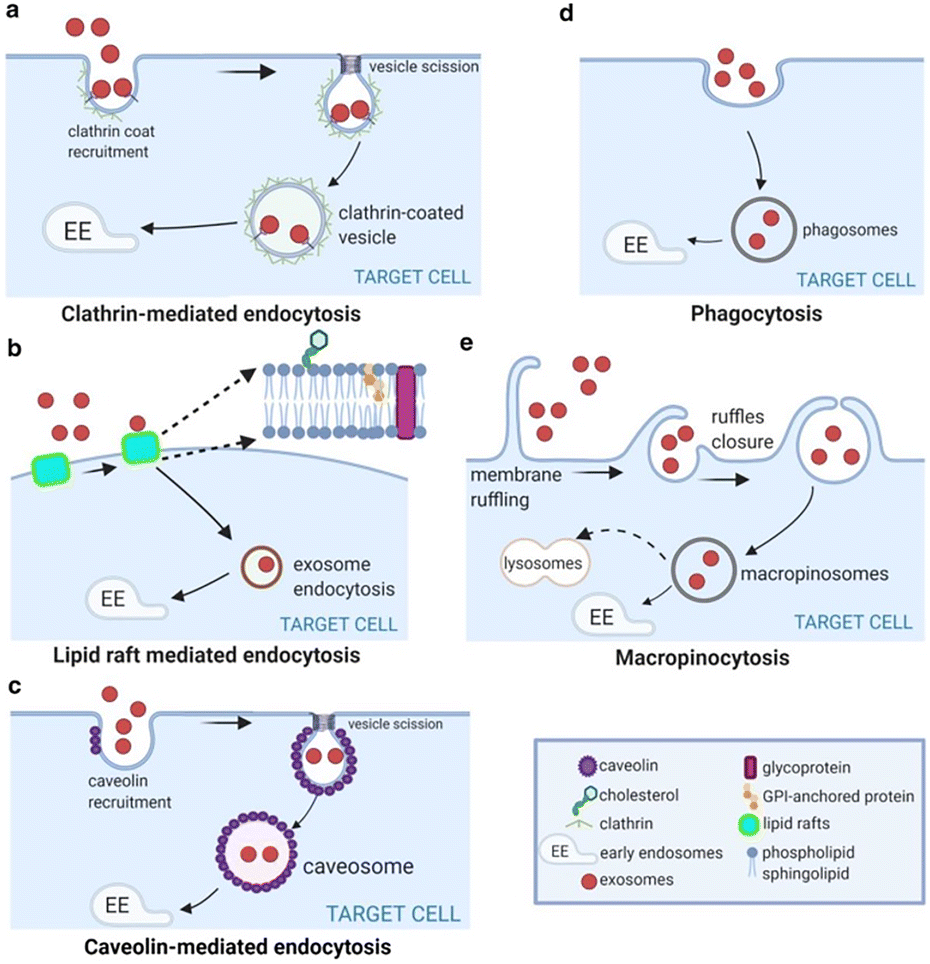
What stands out most in this review is the biological precision that sEVs naturally possess. Unlike synthetic nanoparticles, sEVs inherit surface proteins, lipids, and microRNAs from their parent cells, enabling them to:
-deliver drugs efficiently across the dense hypovascular stroma,
-evade immune clearance due to their biocompatibility,
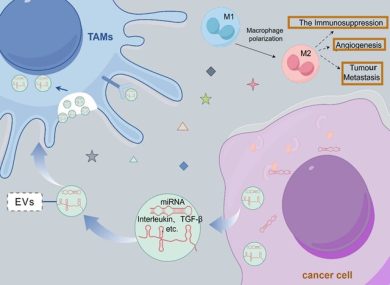
-carry regulatory miRNAs that reshape tumor behavior,
-and selectively target cancer cells with minimal off-target toxicity.
Some of the most striking findings include:
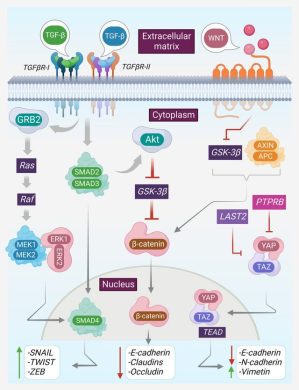
-sEVs from chemo-resistant PC cells transfer resistance traits to other cells (e.g., via EphA2, survivin, miR-210).
-Loading chemotherapeutics into sEVs dramatically increases efficacy, even eliminating tumors in mouse models at doses where free drug is ineffective.
-sEV-based immunotherapies (e.g., galectin-9 siRNA + oxaliplatin-loaded vesicles) reverse immunosuppression and activate cytotoxic T-cell infiltration.
This positions sEVs as uniquely suited for pancreatic cancer, where traditional nanocarriers often fail to penetrate the tumor microenvironment.
Scientific Significance:
sEV-based therapies could shape the future of pancreatic cancer treatment by enabling:
-targeted delivery of chemotherapeutics with higher tumor accumulation,
-engineered loading of siRNAs, miRNAs, and immunomodulators,
-non-invasive biomarker discovery through liquid biopsies,
-and the development of multi-functional platforms (image-guided therapy, stimuli-responsive systems).
While manufacturing challenges and mechanistic gaps remain, the field is moving rapidly toward clinical translation making sEVs one of the most promising tools for tackling a cancer with urgent unmet needs.
Source:
📄 The potential of small extracellular vesicles for pancreatic cancer therapy
RSC Pharmaceutics, 2025
DOI:10.1039/D5PM00115C