🧬 EV-miRNA Communication: A Central Driver of Tumor Progression and Therapy Resistance:
Context:
This comprehensive review highlights how extracellular vesicle–associated microRNAs (EV-miRNAs) function as powerful messengers within the tumor microenvironment (TME).
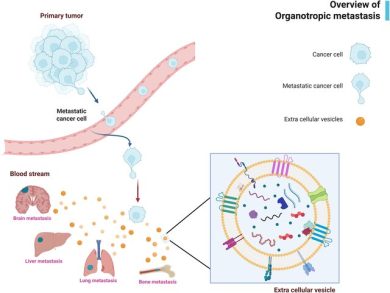
EV-miRNAs orchestrate communication among cancer cells, fibroblasts, immune cells, endothelial cells, and the extracellular matrix shaping nearly every aspect of tumor biology, including proliferation, angiogenesis, metastasis, stemness, metabolic reprogramming, and drug resistance.
Insight:
What stands out in this review is how EV-miRNAs act as precision regulators that rewire cellular behavior across the TME.
Key mechanisms include:
-Promoting tumor growth by suppressing apoptosis and enhancing proliferative signaling.
-Driving EMT and metastasis through miRNAs such as miR-21, miR-10b, miR-200 family, and miR-23a.
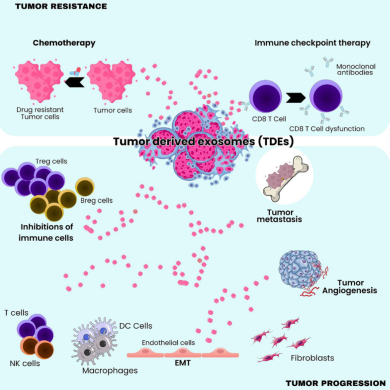
-Reprogramming cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) into pro-tumor modulators of inflammation and matrix remodeling.
-Suppressing antitumor immune activity, including T-cell exhaustion and macrophage M2 polarization.
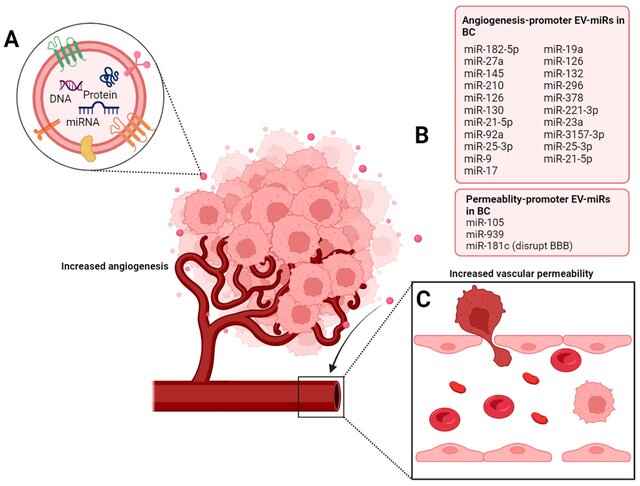
-Inducing angiogenesis via EV-miR-210, EV-miR-9, and EV-miR-130a.
-Contributing to chemoresistance, particularly through miR-21, miR-222/221, miR-155, and miR-214.
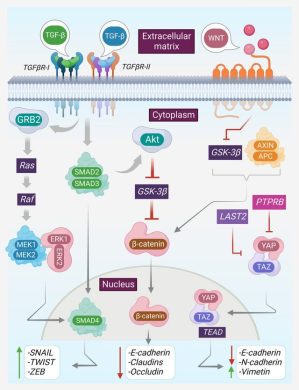
These miRNAs do not act randomly they target specific transcription factors (NF-κB, STAT3, HIF-1α), tumor suppressors (PTEN, PDCD4), and metabolic pathways that enable tumor adaptation.
Scientific Significance:
EV-miRNAs are emerging as transformative tools for cancer biology because they can enable:
-Early cancer detection through liquid biopsy of circulating EV-miRNAs.
-Therapy monitoring by tracking EV cargo modulation during treatment.
-Predictive biomarkers of drug resistance and immunotherapy response.
-Engineered EV-based therapies, delivering miRNA inhibitors, siRNAs, or tumor-suppressive miRNAs.
-Targeting EV biogenesis or uptake pathways as a strategy to disrupt malignant intercellular signaling.
This review reinforces the pivotal role of EV-miRNA communication as a unifying mechanism that drives tumor heterogeneity, immune evasion, and treatment failure.
Source:
📄EV-miRNA-Mediated Intercellular Communication in the Breast Tumor Microenvironment.
DOI:10.3390/ijms241713085